WSC and FVM
|
Hello !
New version (1.2) released! If you are using an older version update now! This page will be improved in next days.
|
Contents
- 1 Getting Started
- 2 WSC Support the C language features
- 3 WSC Error reporting
- 4 Some differences in the WSC with the standard C
- 5 Notice & Tips
- 6 List of library functions
- 6.1 WSC Functions
- 6.1.1 void allclr( void )
- 6.1.2 void areaclr( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
- 6.1.3 void arearev( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
- 6.1.4 void putdisp( void )
- 6.1.5 void setpoint( int x, int y, char kind )
- 6.1.6 int getpoint( int x, ing y )
- 6.1.7 void drawline( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
- 6.1.8 void clearline( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
- 6.1.9 void drawcircle( int x, int y, int r )
- 6.1.10 void fillcircle( int x, int y, int r )
- 6.1.11 void drawbox( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
- 6.1.12 void fillbox( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
- 6.1.13 void locate( int x, int y )
- 6.1.14 void print( char *str )
- 6.1.15 void printxy( int x, int y, char *str, int type )
- 6.1.16 void printmini( int x, int y, char *str, int type )
- 6.1.17 void savedisp( char num )
- 6.1.18 void restdisp( char num )
- 6.1.19 void popupwin( int n )
- 6.1.20 int openfile( const char *name, int mode )
- 6.1.21 int readfile( int handle, void *buf, int size, int readpos )
- 6.1.22 int writefile( int handle, void *buf, int size )
- 6.1.23 int seekfile( int handle, int pos )
- 6.1.24 int closefile( int handle )
- 6.1.25 int getfree( int type, int *freebytes )
- 6.1.26 int getsize( int handle )
- 6.1.27 int createfile( const char *name, int size )
- 6.1.28 int createdir( const char *name )
- 6.1.29 int deletefile( const char *name )
- 6.1.30 int deletedir( const char *name )
- 6.1.31 int getkey( int *keycode )
- 6.1.32 int waitkey( void )
- 6.1.33 int iskeydown( int keycode )
- 6.1.34 void sleep( int millsecond )
- 6.2 File name format
- 6.3 Keycode
- 6.1 WSC Functions
- 7 Feedback
- 8 Changelog
Getting Started
Copy the two files inside the bin folder (WSC.g1a, FVM.g1a) to the calculator. In order to edit the source code on calc, you may need to use the EDITv1.51, of course, you can also edit the source code on the computer, it is plain text.
After the installation is complete, the main menu should be as follows:
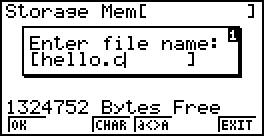
Making a hello world
Open the EDIT, the storage Mem (Warning: Do not use the Main Mem) and create a new document.
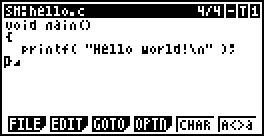
Enter the text:
void main( )
{
printf( “Hello World!\n” );
}
(PS the edit can adjust the font size (shift-set up to enter the setting interface), use the small print on one screen you can see more code, it is recommended to use the small print, set the font size in the optn other Word the wrap is also recommended to choose the offrecommended settings below)
The input is completed as follows:
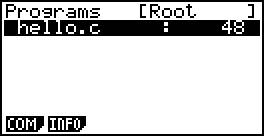
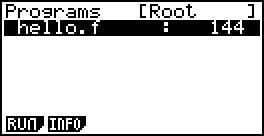
To compile the file, exit, enter the WSC, press the F1 (compile) to compile the source code.
If there are no error, the screen output is done, if there are errors you can return to EDIT to modify. Upon completion any key to exit into the FVM, the F1 (run) the implementation of the bytecode. The screen will output hello world. After the implementation of any key to exit.
WSC Support the C language features
The operator
+ - * / % += -= *= /= < <= > >= == != && || ! != &
Note that the last '&' is the address instead of a bitwise
Data type
Any number of dimensions in an int a char a float array to point to the basic types of pointer (pointer to the array)
Statement
If the else the while for the return the break
Notes
C style / * ........... * / and C + + style / / ...........
The function
Support recursion, a detailed list of library functions, see library.html
Preprocessor
Simple macro replacement (with parameters) a #define, #include (not a real file contains internal use only)
WSC Error reporting
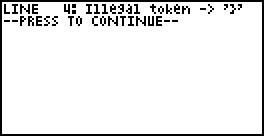
Wsc error reporting is not perfect, calculator small screen is not easy to display all error messages.
Wsc will be displayed on the screen when the error is detected, the error message, as shown:
Then press the menu key you can exit to modify the other key to display the next error message.
Note that WSC did not prompt a warning!
Any pointers, arrays, in its eyes are the same, any assignment.
int, a char, float, assignment, will not generate any warning messages.
Some differences in the WSC with the standard C
Does not require the function declaration
As long as the function is defined in the file, regardless of location, can call anywhere.
Only two scopes
The entire procedure only two scope, global scope and function within the local scope.
void main()
{
int a;
{
int a;
}
}
The example program will receive an error message "Variable 'a' redefinition"
int * a, b;
WSC a and b will be a pointer to int. (It is recommended that written int * a, b; instead of int * a, b;).
int *p; p++;
The actual value of p in the ANSI C plus 4 (sizeof (int)), but WSC will only p plus 1.
char s[50] = “asdfjkl”;
This initialization is not yet supported, sample sentence is wrong.
int a[2][2] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
Int a [2] [2] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
This initialization is not yet supported, sample sentence is wrong. Multidimensional array initialization must be properly grouped, such as
int a[2][2] = { {1, 2}, {3, 4} }; grouped correctly less some elements correctly, such as
int a[2][2] = { {1}, {3} };
Notice & Tips
int a[10];printf( “%d”, a );
The code writer's intent is to obtain the value of a, but as mentioned above, the WSC seen as a type of all pointers, printf library function is overloaded, and the second parameter is a pointer to a function only printf (char *, char *), so the compiler to do a wrong choice, a look has become a char *.
A correct approach is: int a[10]; int t = a; printf( “%d”, t );
char ch;scanf( “%c”, &ch );
For some reason, such an approach to problems, it is recommended to use getchar ();
Enter the uppercase letters
Press F6 in the input interface switch case.
FVM will automatically initialize the random number seed
Does not require the programmer calling the srand ()
Enter the uppercase letters
Press F6 in the input interface switch case
Set up multiple strong back
#progma FORCE_BREAK
Anywhere in the source code to add the above statement, you can hold down the F1 + F2 + F6 to force quit the program execution.
List of library functions
Has now completed most of 9860 to support the c standard functions, the next version will be added to the SDK functions.
printf, sprintf, scanf, sscanf is the overloaded function. Note that they do not have a variable argument list
stdio.h |
int printf( char *format, int val ) |
int printf( char *format, float val ) |
|
int printf( char *format, char* val ) |
|
int sprintf( char *buffer, char *format, int val ) |
|
int sprintf( char *buffer, char *format, float val ) |
|
int sprintf( char *buffer, char *format, char* val ) |
|
int scanf( char *format, int *address ) |
|
int scanf( char *format, float *address ) |
|
int scanf( char *format, char *address ) |
|
int sscanf( char *buffer, char *format, int *address ) |
|
int sscanf( char *buffer, char *format, int *address ) |
|
int sscanf( char *buffer, char *format, float *address ) |
|
int getchar( void ) |
|
int putchar( int c ) |
|
ctype.h |
int isalnum( int c ) |
int isalpha( int c ) |
|
int iscntrl( int c ) |
|
int isdigit( int c ) |
|
int isgraph( int c ) |
|
int islower( int c ) |
|
int isprint( int c ) |
|
int ispunct( int c ) |
|
int isspace( int c ) |
|
int isupper( int c ) |
|
int tolower( int c ) |
|
int toupper( int c ) |
|
math.h |
float acos( float x ) |
float asin( float x ) |
|
float atan( float x ) |
|
float atan2( float x, float y ) |
|
float cos( float x ) |
|
float sin( float x ) |
|
float tan( float x ) |
|
float cosh( float x ) |
|
float sinh( float x ) |
|
float tanh( float x ) |
|
float log( float x ) |
|
float log10( float x ) |
|
float modf( float x, float *y ) |
|
float pow( float x, float y ) |
|
float sqrt( float x ) |
|
float ceil( float x ) |
|
float fabs( float x ) |
|
float floor( float x ) |
|
float fmod( float x, float y ) |
|
stdlib.h |
float atof( char *str ) |
int atoi( char *str ) |
|
int rand( void ) |
|
#define RAND_MAX 32767 |
|
void srand( int seed ) |
|
void *calloc( int nelem, int elsize ) |
|
void *malloc( int size ) |
|
void *calloc( void *ptr, int size ) |
|
void free( void *ptr ) |
|
int abs( int x ) |
|
string.h |
void memcpy( void *p1, void *p2, int n ) |
char *strcpy( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strncpy( char *s1, char *s2, int n ) |
|
char *strcat( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strncat( char *s1, char *s2, int n ) |
|
int memcmp( void *p1, void *p2, int n ) |
|
int strcmp( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
int strncmp( char *s1, char *s2, int n ) |
|
void *memchr( void *p, int c, int n ) |
|
char *strchr( char *s, int c ) |
|
int strcspn( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strpbrk( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strrchr( char *s, int c ) |
|
int strspn( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strstrr( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
void memset( void *s, int c, int n ) |
|
int strlen( char *s ) |
|
void *memmove( void *s1, void *s2, int n ) |
WSC Functions
To use the following functions and definitions, include fxlib.h
All the graphing function draw to VRAM, programmer should use putdisp() to put VRAM to Display Driver.
The range fo abscissa(x) of pointers is from 0 to 127.
The range fo ordinate(y) of pointers is from 0 to 63.
void allclr( void )
Clear the whole area
void areaclr( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Clear the specified area
(x1, y1) is the upper-left conner of rectangle. (x2, y2) is the lower-right corner of rectangle.
void arearev( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Reverses a specified area
(x1, y1) is the upper-left conner of rectangle. (x2, y2) is the lower-right corner of rectangle.
void putdisp( void )
Put all data from VRAM to Display Driver.
void setpoint( int x, int y, char kind )
Set or erase a dot at the specified position.
If you set point to 1 then the dot is made black. If you set point to 0 then the dot is cleared.
int getpoint( int x, ing y )
Checks a dot at the specified position
If the dot at the specified position is black then this function returns 1. If the dot at the specified position is white then this function returns 0.
void drawline( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Draws a line from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2)
void clearline( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Draws a white line from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2)
void drawcircle( int x, int y, int r )
Draws a circle at (x,y)
void fillcircle( int x, int y, int r )
Draws a filled circle at (x,y)
void drawbox( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Draws a box, (x1, y1) is the upper-left conner of rectangle. (x2, y2) is the lower-right corner of rectangle.
void fillbox( int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2 )
Draws a filled box, (x1, y1) is the upper-left conner of rectangle. (x2, y2) is the lower-right corner of rectangle.
void locate( int x, int y )
Makes settings for the location of the display cursor
The range of x is from 1 to 8, the range of y is from 1 to 21 here.
void print( char *str )
Displays a character string at the current position of the display cursor
void printxy( int x, int y, char *str, int type )
Displays a character string at the specified position.
If you set the type to 0 then the character string is displayed in normal color. If you set the type to 1 then the character string is displayed in reverse color.
void printmini( int x, int y, char *str, int type )
Displays a small font character string at the specified position.
The following definitions are declared for type:
| MINI_OVER | Overwrite (fill) |
| MINI_OR | OR |
| MINI_REV | Reverse color |
| MINI_REVOR | OR in reverse color |
( printmini( 1, 1, “hello”, MINI_OVER ); )
void savedisp( char num )
Saves a screen image in the system area.
Num is the ID of the save area. It can only be SAVEPAGE1, SAVEPAGE2 or SAVEPAGE3.
( savedisp( SAVEPAGE1 ); )
void restdisp( char num )
Restores a screen image in the system area.
Num is the ID of the save area. It can only be SAVEPAGE1, SAVEPAGE2 or SAVEPAGE3.
( restdisp( SAVEPAGE1 ); )
void popupwin( int n )
Displays a popup window of the specified size of lines. Also, the inside of the popup window is cleared.
The range of n is from 1 to 5.
int openfile( const char *name, int mode )
opens an existing file
name is the file name (File Name Format)
mode specifies the action to open. The following definitions are declared for open mode.
| OPEN_R | Read |
| OPEN_W | Write |
| OPEN_RW | Read and write |
If the function succeeds, the return value specifies a file handle. It is greater than or equal to 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int readfile( int handle, void *buf, int size, int readpos )
handle is the return value of openfile()
size is the bytes to be read from the file.
readpos is the starting position to read. If the readpos parameter is -1, this functi on reads data from the position last read ended. If the readpos parameter greater than or equal to 0, this function reads data from the position indicated by the readpos parameter.
If the function succeeds, this function returns the number of bytes actually read. It is greater than or equal to 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int writefile( int handle, void *buf, int size )
handle is the return value of openfile()
If the function succeeds, this function returns the number of bytes actually read. It is greater than or equal to 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int seekfile( int handle, int pos )
moves the file pointer of an open file
If the function succeeds, this function returns the number of bytes that can continuously be read. It is greater than or equal to 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int closefile( int handle )
closes an open file handle
int getfree( int type, int *freebytes )
retrieves the size of the free space, in bytes, of the specified device
The following definitions are declared for type.
| MAIN_FREE | main memory |
| STO_FREE | storage memory |
| SD_FREE | sd card |
( getfree( SD_FREE, &size ); )
freebytes is the pointer to the size of the free space
If the function succeeds, this function returns 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int getsize( int handle )
retrieves the size, in bytes, of the specified file.
int createfile( const char *name, int size )
Creates a file (View File Name Format)
If the function succeeds, the return value is 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int createdir( const char *name )
Creates a directory (View File Name Format)
If the function succeeds, the return value is 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int deletefile( const char *name )
Delete a file (View File Name Format)
If the function succeeds, the return value is 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int deletedir( const char *name )
Delete a directory (View File Name Format)
If the function succeeds, the return value is 0.
If the function fails, the return value is an error code. It is a negative value.
int getkey( int *keycode )
Performs a key wait and returns a value indicating the pressed key
If there are no characters in the key buffer, this func tion waits until a character arrives and then returns immediately.
Even if the menu key pressed, this function does not return menu key code. The system processes the menu key event.
Off event, Auto Power Off event, and contrast adjustment are also handled by this function. If an off or Auto Power Off event occurs the application will not be notified. Once the calculator is turned back on control is returned to the GetKey function.
If a character key was pressed, the return value is 1.
If a control key was pressed, the return value is 0.
int waitkey( void )
Wait for a key, and return the key code.
It is a simplify of getkey
(View key code)
int iskeydown( int keycode )
Checks whether the specified key is pressed.
The parameter is a key code of the key that you check.
When you wait events only by this function, the calculator never turns off. Only use this function when you need to wait for key input to continue.
If the specified key is pressed, the return value is 1.
If the specified key is not pressed, the return value is 0.
(View key code)
void sleep( int millsecond )
Suspends the execution of the current thread for a specified interval.
File name format
A few examples to illustrate the format of the file name:
File named 2.txt in the Storage Mem in the root directory is "\\\\fls0\\2.txt"
File named 2.txt in the directory book in the Storage Mem is "\\\\fls0\\book\\2.txt"
File named 2.txt in the root directory of the SD card is "\\\\crd0\\2.txt"
Directory book in SD card is "\\\\crd0\\book"
Can not handle files in the Main Mem.
Note that the filename is case sensitive!
You can see some files usage exemple in \doc\exemple\FILE.c
Keycode
fxlib.h defined for several commonly used keys more convenient macro
#define KEY_UP 30018 #define KEY_DOWN 30023 #define KEY_LEFT 30020 #define KEY_RIGHT 30021 #define KEY_EXIT 30002 #define KEY_AC 30015 #define KEY_DEL 30025 #define KEY_EXE 30024 #define KEY_SHIFT 30006 #define KEY_ALPHA 30007 #define KEY_MENU 30003 #define KEY_OPTN 30008 #define KEY_F1 30009 #define KEY_F2 30010 #define KEY_F3 30011
You can see other key codes in the \doc\example\KEYCODE.c
Feedback
If you found bugs, or have any suggestions, questions, you can post it at WSC and FVM Thread.
Special thanks to yangsc825 (testing and recommendations), helder7 (English documentation), Kenneth C. Louden ("Compiler Construction Principles and Practice").
Changelog
* 21-06-2012 version 1.2
- Add a simple pre-processor (now the #include)
- Add file manipulation and plotting functions
- Add to the bond strength rewind functions
- Add an optimized technology, test data, maximum speed increased by 10%
- Fixed some errors in the parameter passing
- Fix array initialization can only occur once error
- Fixed the error of the multidimensional array address
- Others...
* 07-06-2012 version 1.1
- Add most of 9860 to support the standard C function
- Add a full description of document
- Add multi-dimensional array initialization
- Add transfer the character '\ t'
- Improve the stdio, to support multi-line input, uppercase letters
- Improve the error message, more friendly
- Fixed main, not the return 0 mistakes
- Fixed errors in some of the parameters passed
- Fixed a global variable, function, character constants can not be the same name error
- Repair evaluation stack stack stack error
- Other
* 28-05-2012 version 1.0
- Preview Release