WSC and FVM
Contents
Getting Started
Copy the two files inside the bin folder (WSC.g1a, FVM.g1a) to the calculator. In order to edit the source code on calc, you may need to use the EDITv1.51, of course, you can also edit the source code on the computer, it is plain text.
After the installation is complete, the main menu should be as follows:
Making a hello world
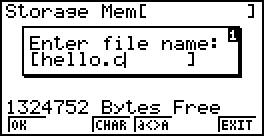
Open the EDIT, the storage Mem (Warning: Do not use the Main Mem) and create a new document.
Enter the text:
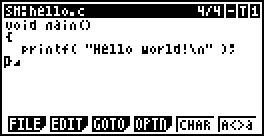
void main( )
{
printf( “Hello World!\n” );
}
(PS the edit can adjust the font size (shift-set up to enter the setting interface), use the small print on one screen you can see more code, it is recommended to use the small print, set the font size in the optn other Word the wrap is also recommended to choose the offrecommended settings below)
The input is completed as follows:
To compile the file, exit, enter the WSC, press the F1 (compile) to compile the source code.
If there are no error, the screen output is done, if there are errors you can return to EDIT to modify. Upon completion any key to exit into the FVM, the F1 (run) the implementation of the bytecode. The screen will output hello world. After the implementation of any key to exit.
WSC Support the C language features
The operator
+ - * / % += -= *= /= < <= > >= == != && || ! != &
Note that the last '&' is the address instead of a bitwise
Data type
Any number of dimensions in an int a char a float array to point to the basic types of pointer (pointer to the array)
Statement
If the else the while for the return the break
Notes
C style / * ........... * / and C + + style / / ...........
The function
Support recursion, a detailed list of library functions, see library.html
Preprocessor
Simple macro replacement (with parameters) a #define, #include (not a real file contains internal use only)
WSC Error reporting
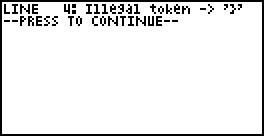
Wsc error reporting is not perfect, calculator small screen is not easy to display all error messages.
Wsc will be displayed on the screen when the error is detected, the error message, as shown:
Then press the menu key you can exit to modify the other key to display the next error message.
Note that WSC did not prompt a warning!
Any pointers, arrays, in its eyes are the same, any assignment.
int, a char, float, assignment, will not generate any warning messages.
Some differences in the WSC with the standard C
Does not require the function declaration
As long as the function is defined in the file, regardless of location, can call anywhere.
Only two scopes
The entire procedure only two scope, global scope and function within the local scope.
void main()
{
int a;
{
int a;
}
}
The example program will receive an error message "Variable 'a' redefinition"
int * a, b;
WSC a and b will be a pointer to int. (It is recommended that written int * a, b; instead of int * a, b;).
int *p; p++;
The actual value of p in the ANSI C plus 4 (sizeof (int)), but WSC will only p plus 1.
char s[50] = “asdfjkl”;
This initialization is not yet supported, sample sentence is wrong.
int a[2][2] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
Int a [2] [2] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
This initialization is not yet supported, sample sentence is wrong. Multidimensional array initialization must be properly grouped, such as
int a[2][2] = { {1, 2}, {3, 4} }; grouped correctly less some elements correctly, such as
int a[2][2] = { {1}, {3} };
Notice
int a[10];printf( “%d”, a );
The code writer's intent is to obtain the value of a, but as mentioned above, the WSC seen as a type of all pointers, printf library function is overloaded, and the second parameter is a pointer to a function only printf (char *, char *), so the compiler to do a wrong choice, a look has become a char *.
A correct approach is int a [10]; int t = a; printf ("% d", t);
char ch;scanf( “%c”, &ch );
For some reason, such an approach to problems, it is recommended to use getchar ();
Enter the uppercase letters
Press F6 in the input interface switch case.
List of library functions
Has now completed most of 9860 to support the c standard functions, the next version will be added to the SDK functions.
printf, sprintf, scanf, sscanf is the overloaded function. Note that they do not have a variable argument list
stdio.h |
int printf( char *format, int val ) |
int printf( char *format, float val ) |
|
int printf( char *format, char* val ) |
|
int sprintf( char *buffer, char *format, int val ) |
|
int sprintf( char *buffer, char *format, float val ) |
|
int sprintf( char *buffer, char *format, char* val ) |
|
int scanf( char *format, int *address ) |
|
int scanf( char *format, float *address ) |
|
int scanf( char *format, char *address ) |
|
int sscanf( char *buffer, char *format, int *address ) |
|
int sscanf( char *buffer, char *format, int *address ) |
|
int sscanf( char *buffer, char *format, float *address ) |
|
int getchar( void ) |
|
int putchar( int c ) |
|
ctype.h |
int isalnum( int c ) |
int isalpha( int c ) |
|
int iscntrl( int c ) |
|
int isdigit( int c ) |
|
int isgraph( int c ) |
|
int islower( int c ) |
|
int isprint( int c ) |
|
int ispunct( int c ) |
|
int isspace( int c ) |
|
int isupper( int c ) |
|
int tolower( int c ) |
|
int toupper( int c ) |
|
math.h |
float acos( float x ) |
float asin( float x ) |
|
float atan( float x ) |
|
float atan2( float x, float y ) |
|
float cos( float x ) |
|
float sin( float x ) |
|
float tan( float x ) |
|
float cosh( float x ) |
|
float sinh( float x ) |
|
float tanh( float x ) |
|
float log( float x ) |
|
float log10( float x ) |
|
float modf( float x, float *y ) |
|
float pow( float x, float y ) |
|
float sqrt( float x ) |
|
float ceil( float x ) |
|
float fabs( float x ) |
|
float floor( float x ) |
|
float fmod( float x, float y ) |
|
stdlib.h |
float atof( char *str ) |
int atoi( char *str ) |
|
int rand( void ) |
|
void srand( int seed ) |
|
void *calloc( int nelem, int elsize ) |
|
void *malloc( int size ) |
|
void *calloc( void *ptr, int size ) |
|
void free( void *ptr ) |
|
int abs( int x ) |
|
string.h |
void memcpy( void *p1, void *p2, int n ) |
char *strcpy( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strncpy( char *s1, char *s2, int n ) |
|
char *strcat( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strncat( char *s1, char *s2, int n ) |
|
int memcmp( void *p1, void *p2, int n ) |
|
int strcmp( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
int strncmp( char *s1, char *s2, int n ) |
|
void *memchr( void *p, int c, int n ) |
|
char *strchr( char *s, int c ) |
|
int strcspn( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strpbrk( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strrchr( char *s, int c ) |
|
int strspn( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
char *strstrr( char *s1, char *s2 ) |
|
void memset( void *s, int c, int n ) |
|
int strlen( char *s ) |
|
void *memmove( void *s1, void *s2, int n ) |
Feedback
You can give your feedback in the WSC and FVM Thread
Changelog
* 07-06-2012 version 1.1
- Add most of 9860 to support the standard C function
- Add a full description of document
- Add multi-dimensional array initialization
- Add transfer the character '\ t'
- Improve the stdio, to support multi-line input, uppercase letters
- Improve the error message, more friendly
- Fixed main, not the return 0 mistakes
- Fixed errors in some of the parameters passed
- Fixed a global variable, function, character constants can not be the same name error
- Repair evaluation stack stack stack error
- Other
* 28-05-2012 version 1.0
- Preview Release